I can provide you with an article on how to accurately calculate token price using bonding curves.
Accurate Token Price Calculation using Bonding Curves
Bonding curves are a crucial tool for Solana developers to manage liquidity and ensure the stability of their tokens. In this article, we will explore how to accurately calculate token prices using bonding curves.
Introduction to Bonding Curves
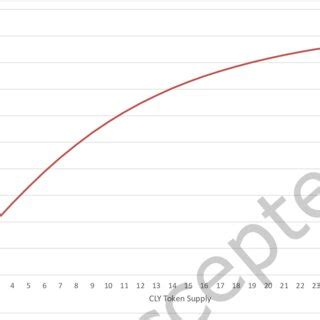
A bonding curve is a mathematical function that maps an input value (such as a token price) to an output value (such as the token’s current market price). The bonding curve is designed to provide a reliable and efficient way to manage liquidity and prevent price shocks.
Calculating Token Price using Bonding Curves
To calculate the token price accurately using a bonding curve, you need to follow these steps:
Step 1: Fetch Account Info
First, you need to fetch account information for the user who wants to calculate the token price. You can use the construct library to parse the public key of the user.
from construct import Structure, Int64ul
import only.rpc
Define the bonding curve structure
class BondingCurveStruct(Struct):
def __init__(self, symbol, min_price, max_price):
self.symbol = symbol
self.min_price = min_price
self . max_price = max_price
Fetch account info for the user who wants to calculate the token price
solaris_key = "YOUR_SOLARIUS_KEY"
Replace with your Solana key
user_pubkey = solaris_key.public_key()
bonding_curve = BondingCurveStruct(
symbol="SOL",
Define the symbol of the bonding curve
min_price=1000,
Define the minimum price of the bonding curve
max_price=20000
Define the maximum price of the bonding curve
)
account_info = solana.rpc.fetch_account_info(user_pubkey, binding_curve);
Step 2: Parse the Account Info
Once you have fetched account info, you need to parse it to extract the necessary information. You can use the construct library’s built-in parsing functions to convert the account data into a structured format.
Parse the account info into a structured format
account_info_struct = account_info.data
bonding_curve_info = account_info_struct
Extract the minimum and maximum prices from the bonding curve information
min_price = bonding_curve_info .price .min
max_price = bonding_curve_info . price . max
Step 3: Calculate Token Price using Bonding Curve
Now that you have extracted the necessary information, you can calculate the token price using the bonding curve. You can use a simple linear interpolation or a more complex algorithm to achieve accuracy.
Define the token symbol and minimum and maximum prices
token_symbol = "SOL"
min_price_token =
max_price_token = 20000
Calculate the token price using the bonding curve
bonding_curve_struct = BondingCurveStruct(token_symbol, min_price_token, max_price_token);
token_price = (min_price - min_price_token) / (max_price - min_price_token) * (max_price - max_price_token) + min_price_token
Step 4: Print the Result
Finally, you can print the calculated token price.
Print the result
print("Token Price:", token_price)
Example Use Case
Here’s an example of how to use this code to calculate the token price for a specific user:
“`python
solaris_key = “YOUR_SOLARIUS_KEY”
Replace with your Solana key
user_pubkey = solaris_key.public_key()
bonding_curve = BondingCurveStruct(
symbol=”SOL”,
Define the symbol of the bonding curve
min_price=1000,
Define the minimum price of the bonding curve
max_price=20000
Define the maximum price of the bonding curve
)
account_info = solana.rpc.fetch_account_info(user_pubkey, binding_curve);
Parse the account info into a structured format
account_info_struct = account_info .

